Treating Eczema vs. Atopic Dermatitis
Dermatitis is an umbrella term that describes a variety of skin inflammation. Atopic dermatitis is a term that refers to “atopic” or hereditary, which means the condition typically runs in the families and usually occur in conjunction with hay fever, asthma and allergies. Dermatitis can occur at on almost any area of the body, and there are can be many different causes for its occurrence. Dermatitis may develop as an itchy rash or red patches of swollen skin or it may form blisters that ooze, flake off, and become scaly in nature.
Eczema, on the other hand, is a very general word that describes one from of dermatitis. Eczema symptoms often vary greatly from person to person depending on health and age. Although it’s not contagious, the following symptoms are often uncomfortable and embarrassing, for instance:
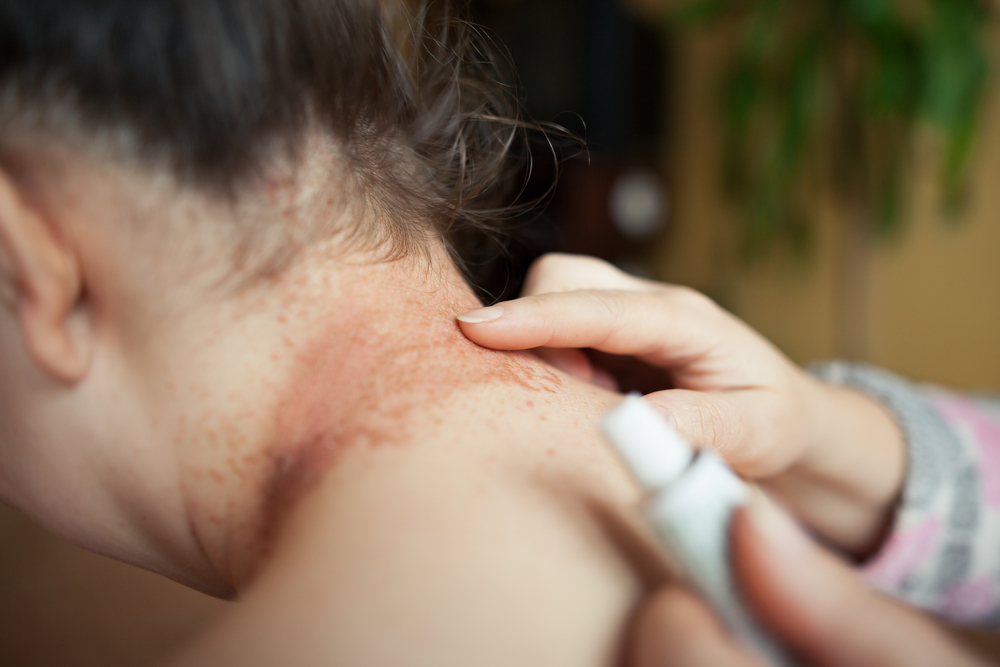
- In infants, rashes may appear on the cheeks and scalp.
- The rashes initially transform into a bubble and later discharge fluid.
- Eczema is extremely itchy and may disrupts sleep in infants.
- In adults, eczema can occur on any part of the body, however, it’s most common on the neck, between the fingers and toes, around the eyes, and face.
- In adults, eczema becomes dry, scaly, and itchy patches of skin.
- As the rashes increase, the itchiness becomes more persistent.
- In some cases, these rashes may result in other skin infections.
Treating eczema
While there is no permanent cure for Eczema, proper and ongoing treatments can help in reducing symptoms and controlling the frequency of flare ups.
Medication is often recommended by doctors to control the spread of the rashes and also to reduce the itching and other uncomfortable symptoms. It is very important to treat eczema to prevent infections.
In addition to medication, there are many things patients can do at home to improve their quality of life and decrease flare ups. Lifestyle tips may include:
- Having baths with lukewarm water
- Moisturizing every day
- Using mild soap with no fragrance for sensitive skin
- Wearing breathable cotton cloth
- Staying cool and comfortable to prevent sweat and skin irritation
Symptoms of atopic dermatitis
Similar to eczema, the following symptoms of atopic dermatitis also vary from person to person:
- Dry skin
- Severe itching that worsens during the night time
- Brownish or reddish gray patches on the eet, chest, neck, wrist and eyelids, etc.
- Small blisters or bumps, which leak fluid if scratched.
- Scaly skin
- Swollen skin
Treating dermatitis
Medication is the first step towards treating this problem. Your doctor will recommend oral pills and topical creams that can help in treating itching and infections. Therapies can also be used for treating the problem. Therapies like light therapy, wet dressing and a good rest to the body can make some difference.


